Can I run FastChip 2.x from the command line?
Some designers prefer to use command line-driven or batch-
oriented programs. Others prefer to avoid a graphical interface
unless absolutely required. FastChip 2.x provides a non-graphical, command-line
capability. FastChip commands are executed by opening a
Windows DOS box or command prompt. The method to open
a DOS box or command prompt depends upon the version of Windows
installed on your computer.
Documentation on using the command-line interface is available
in Command_Line_Tools_Users_Guide.pdf, located under the
FastChip installation directory in the following path … \Fastchip\Docs\Triscend Tool Processes There are a few advantages to using the command line option. · Directly execute the desired FastChip function.· Gain access to options unavailable from the FastChip graphical
interface.· Reduce overall memory requirements while using FastChip.· Execute multiple FastChip command-line functions from a user-
defined DOS batch program or using various Make utilities.· Download a configuration image using a low-end computer.  To see a list of available options, type the following at the command prompt:
To see a list of available options, type the following at the command prompt: csoc <Enter>
This command launches the FastChip 'csoc' environment, which
might take a few seconds to load. Without any command-line
arguments, 'csoc' displays the available options.
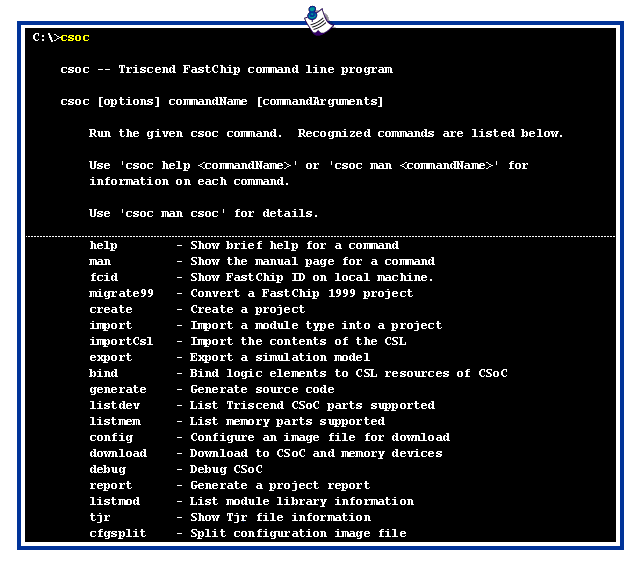
For a quick summary of a 'csoc' command, type the following at the command prompt:
csoc help <command_name> <Enter>
For a detailed
description of all options and usage, type the following at the command prompt:
csoc man <command name> <Enter>